Do you suffer from annoying pain in your buttocks? Do you feel a painful bump near the anus that makes it difficult to sit? You might have an anorectal abscess!
What is an Anorectal Abscess?
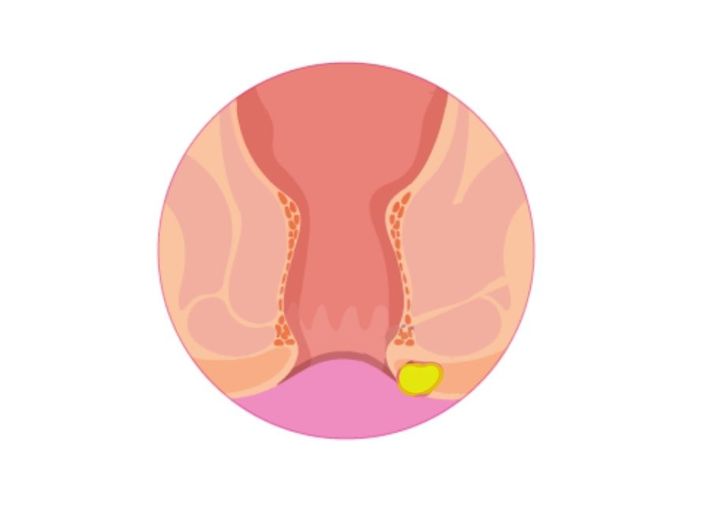
An anorectal or rectal abscess is a large, pus-filled bump located near the anus or inside the rectum. It is extremely painful, to the point that the patient may not be able to sit or sleep comfortably. (1)
An abscess occurs when one of the glands around the anus becomes blocked with bacteria or stool, leading to infection and the accumulation of pus and fluids, forming a very painful abscess. In most cases, treatment requires a simple procedure performed in a doctor’s clinic to drain the abscess. (1)
Causes of Anorectal Abscess
Anorectal abscesses can occur in anyone, but they are more common in men aged 20–60 years. Several factors increase the risk of developing one: (2)
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea: Irritates and inflames the area.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases: Such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease.
- Diabetes: Weakens the immune system and increases infection risk.
- Pregnancy: Causes changes that may increase susceptibility to infections.
- Smoking: Negatively affects blood circulation and immunity.
- Certain medications that suppress the immune system: Such as corticosteroids or chemotherapy.
- Sexually transmitted infections: Can cause infections near the anus.
- Anal gland inflammation (fistula-related inflammation): Small pockets in the intestinal wall can become infected.
Symptoms of Anorectal Abscess
The main symptom is a very painful lump or bump near the anus (sometimes internal in the rectum and not visible). It is usually red, tender, and the pain worsens when sitting, coughing, or defecating. (3)
Other symptoms may include:
- Pus or discharge from the anus
- Swelling or a hard mass near the anus
- Pain during bowel movements
- Rectal bleeding
- Lower abdominal pain
- Fever and chills in some cases
Get relief from abscess pain! Our general surgery team at Al Ahli Hospital is ready to assist you anytime. Book your appointment now.
How is an Anorectal Abscess Diagnosed?
Usually, the doctor can see the abscess during a physical examination in the clinic. They may also perform a digital rectal exam, using a lubricated finger to check for any internal abscesses in the rectum. (3)
Treatment of Anorectal Abscess
- Drainage: Most anorectal abscesses are drained by a doctor in a simple in-clinic procedure using local anesthesia and a small incision.
- Surgery: If the abscess is internal, it may require a surgical procedure in a hospital under anesthesia. (2)
- Antibiotics: After drainage, antibiotics are usually prescribed for about a week to completely eliminate infection and prevent recurrence. (2)
- Post-procedure care: May include:
- Sitz baths to soothe and disinfect the area
- Pain relief medications as prescribed
- Topical ointments for temporary relief
- Keeping the area clean and dry
- Stool softeners to help healing (2)
Can I Treat an Anorectal Abscess at Home?
No, do not attempt to drain the abscess yourself. Even if it appears simple, the infection may be deep and spread to other areas. (2)
If the abscess bursts on its own, clean the area thoroughly with soap and water, cover it with a dressing, and see a doctor to ensure the infection is completely treated. (2)
Anorectal Abscess vs. Anorectal Fistula
- Anorectal abscess: An inflamed, pus-filled cavity near the anus or rectum. (4)
- Anorectal fistula: Usually develops if an abscess is not properly treated. It forms a small tunnel from inside the rectum to the skin near the anus. About 50% of people with an anorectal abscess may develop a fistula.
This highlights the importance of early and proper medical treatment. (4)
References
- University of Rochester Medical Center - Anorectal Abscess
- Cleveland Clinic - Perianal Abscess
- Johns Hopkins Medicine - Anorectal Abscess
- The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons - Abscess and Fistula