Different heart tests help clarify the structure and function of the heart, detect various cardiac problems, and guide appropriate treatment. One of the most common and well-known tests is the echocardiogram (echo).
1. What is an echocardiogram?
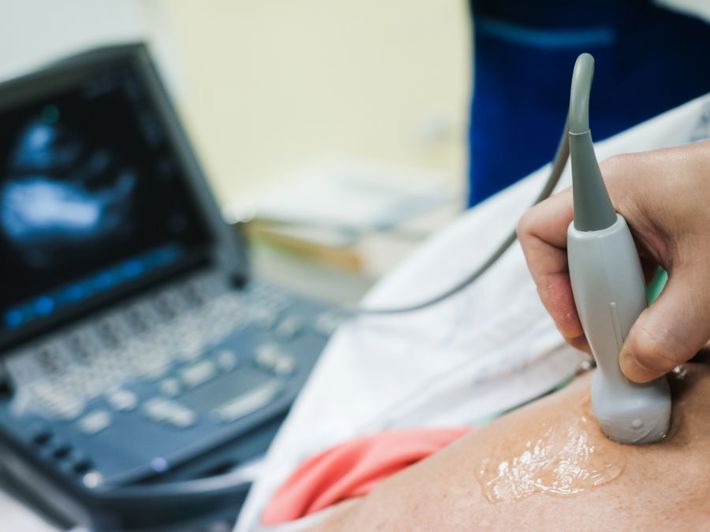
An echocardiogram (Echo) is a very simple test that uses ultrasound waves to create a moving image of the heart. This allows the doctor to see the heart’s contractions, valve function, and other aspects on a nearby screen. It is somewhat similar to a pregnancy ultrasound, but it images the heart instead of the abdomen.(1)
2. Why is an echocardiogram performed?
Your doctor may order an echocardiogram if there is suspicion of heart valve problems, weakened heart muscle, or other cardiac issues, especially if you experience symptoms such as shortness of breath,fast or slow heartbeats,chest pain, or abnormal heart sounds detected during a physical exam. Echo helps identify the cause of these symptoms.(2)
You may also need an echocardiogram before surgery to check your heart’s condition or to monitor an existing heart condition or treatment.(2)
At Al-Ahli Hospital, the Cardiology Department is equipped with advanced technology to detect even minor heart problems with high skill and precision.
3. What does an echocardiogram show?
An echocardiogram can reveal: (3)
- The size and shape of the heart, and whether it is smaller or larger than normal.
- The overall heart function, including the strength of contractions, blood pumping efficiency, and valve performance.
- Weak areas of the heart muscle that do not function properly.
- Heart valve problems, such as regurgitation or stenosis.
- Other issues, such as congenital defects (e.g., holes in the heart), infections, tumors, major blood vessel problems, or areas damaged after a heart attack.
- How your heart responds to certain prescribed treatments.
4. How is the test performed?
No special preparation or fasting is required for a standard echocardiogram.
The procedure usually takes 15 minutes to an hour and is simple and painless. Steps include: (3)
- Preparation and positioning: You will remove your upper clothing and lie on the examination table.
- ECG monitoring (if needed): Adhesive electrodes may be placed on your chest to record electrical activity, helping provide a complete assessment.
- Applying gel: A small amount of gel is applied to your chest to help transmit ultrasound waves.
- Performing the echo: The doctor moves the ultrasound probe over your chest. You may be asked to change positions or hold your breath briefly to get different heart angles.
- Reviewing results: The device displays live video of your heart on a screen for the doctor to analyze and write the medical report.
Specialized types of echocardiograms include transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), which provides more precise images from inside the body using a probe passed through the esophagus under sedation. For TEE, fasting before the test is required. (1)
5. Are there any risks?
Standard echocardiograms are very safe, painless, and do not use any radiation. There are no side effects.(4)
For TEE, you may experience mild throat irritation or coughing during the procedure. Rare complications include difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, minor bleeding, or injury to the esophagus or nearby structures.(4)
6. Echocardiogram vs. ECG
An echocardiogram provides a detailed moving image of the heart, whereas an ECG (electrocardiogram) records the electrical activity of the heart as wavy lines on a screen. (1)
Feature | Echocardiogram | ECG (Electrocardiogram) |
Type | Imaging test | Electrical test |
Measures | Moving image of heart structure and function | Heart’s electrical activity |
Method | Ultrasound waves | Adhesive electrodes |
Detects | Heart muscle disease, valve problems, congenital defects, etc. | Arrhythmias, heart attacks, some heart muscle diseases |
References
- BHF - Echocardiogram
- BHF - What is an echocardiogram?
- American Heart Association - Echocardiogram (Echo)
- Mayo Clinic - Echocardiogram